The Northern Lights, or Aurora Borealis, are a stunning dance of colourful lights, often in shades of green, pink, and purple, painting the heavens. For centuries, these mesmerising displays have charmed people around the world with their beauty and mystery. But what exactly are the Northern Lights, and what causes them to light up the night sky? Let's explore this enchanting natural phenomenon.
Jump to:
What are the Northern Lights?
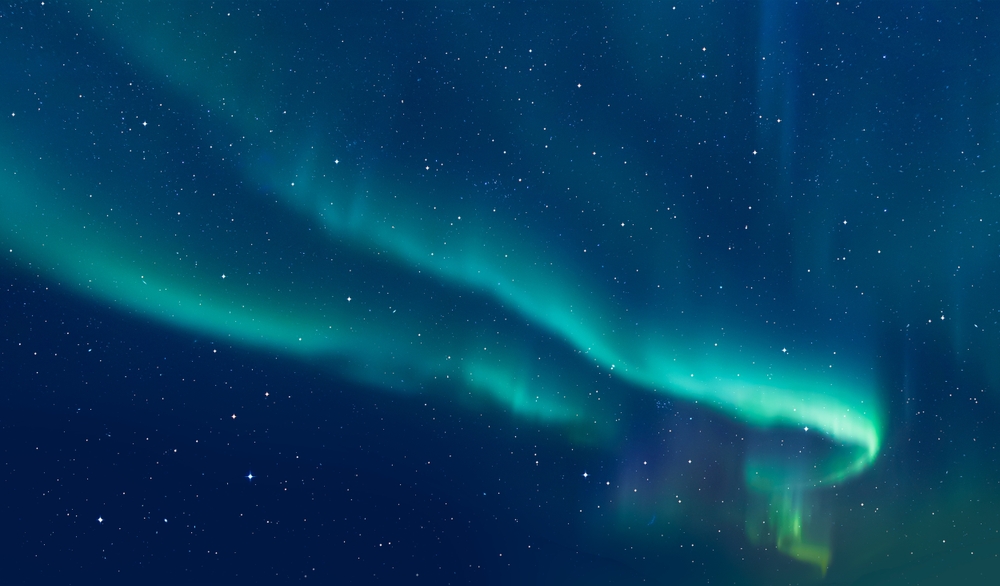

The Northern Lights, scientifically known as Aurora Borealis, are a natural light display predominantly seen in high-latitude regions around the Arctic and Antarctic. These lights are created when charged particles from the sun interact with the Earth's atmosphere, producing vivid and colourful light displays.
Recommended for you!
Best SellersThe Science Behind the Northern Lights
How are the Northern Lights Formed?
The Northern Lights are formed through a fascinating interplay between the sun and the Earth. The sun emits a continuous stream of charged particles known as the solar wind. When these particles reach the Earth, they are drawn towards the poles by the planet's magnetic field. As they collide with gases in the Earth's atmosphere, such as oxygen and nitrogen, they release energy in the form of light, creating the stunning Aurora Borealis.
What Makes the Northern Lights?
The colours of the Northern Lights are determined by the type of gas particles involved in the collisions. Oxygen at higher altitudes produces green and red lights, while nitrogen results in purples, blues, and pinks. The variations in colour are also influenced by altitude and the energy of the incoming solar particles.
Why Do the Northern Lights Happen?
The Northern Lights occur primarily around the polar regions due to the Earth's magnetic field, which is strongest near the poles. This magnetic field channels the solar particles towards these areas, making the lights more frequent and intense.
How Does the Aurora Borealis Work?
The aurora borealis works like a giant cosmic light show. When solar particles collide with the Earth's magnetic field, they are accelerated towards the poles. These particles then collide with atoms and molecules in the Earth's atmosphere, exciting them to higher energy states. As these atoms and molecules return to their normal states, they release photons, or light particles, creating the luminous auroras we see.
What is a Geomagnetic Storm?
A geomagnetic storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a surge in solar wind and magnetic fields. These storms can enhance the visibility and intensity of the Northern Lights, making them visible at lower latitudes than usual.
Geomagnetic Storm Effects on Humans
Geomagnetic storms can cause minor health issues for some people, such as increased anxiety or confusion, but these effects are generally not severe. The main concern remains their impact on technology and communication systems.
Solar Activity: The Source of Northern Lights
Solar Storm in Space
A solar storm occurs when there is a significant release of energy from the sun in the form of solar flares or coronal mass ejections. These events send large numbers of charged particles into space, some of which reach the Earth and contribute to the formation of the Northern Lights.
Solar Hurricanes and Flares
Occasionally, the sun experiences periods of increased activity, leading to solar hurricanes or massive solar flares. These can have a pronounced effect on the Northern Lights, making them more vibrant and widespread. They can also impact satellites and communication systems on Earth.
Solar Storms Effects on Humans
While solar storms can create beautiful auroras, they can also have various effects on human activities. For instance, they can interfere with satellite communications, GPS signals, and even power grids. However, they do not pose a direct threat to human health.
Experiencing the Northern Lights
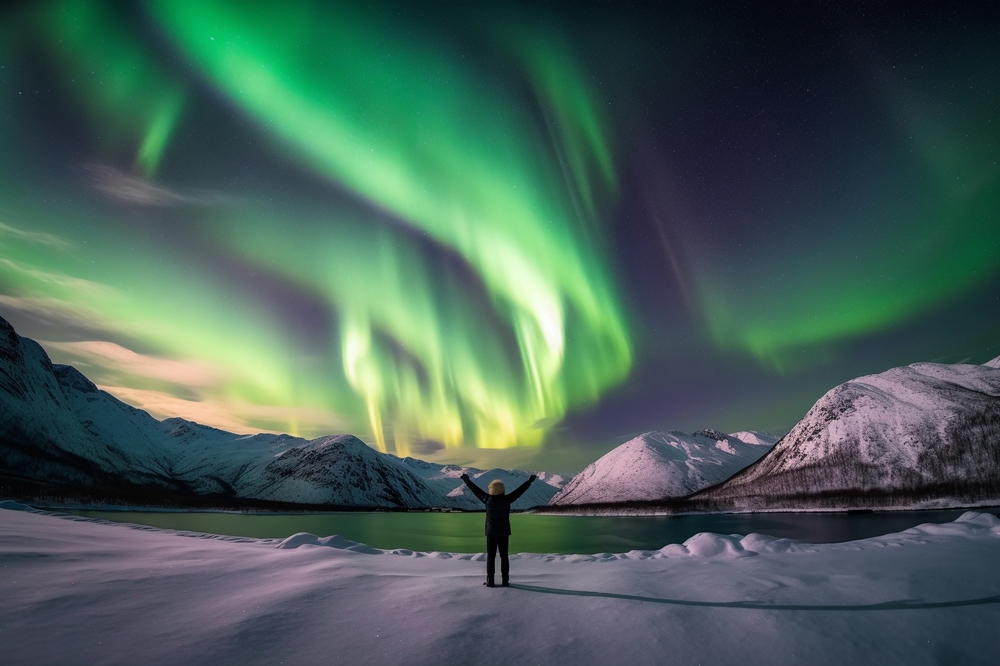

Best Time of Year to See the Northern Lights
The optimal time to see the Northern Lights is during the winter when nights are long and the skies are dark. Peaks in solar activity, known as solar maximum periods, also enhance your chances of seeing more intense displays.
Where and When to See the Northern Lights
Prime locations for viewing the Northern Lights include regions within the "auroral oval" – a ring-shaped zone around the poles where auroras are most likely to occur. This includes countries like Norway, Sweden, Finland, Iceland, Canada, and parts of Alaska. Late autumn to early spring provides the best conditions for aurora viewing.
Can you see the Northern Lights in the UK?
It is possible to see the Northern Lights in the UK, particularly in Scotland and northern England. The best chances occur during periods of high solar activity and clear, dark skies. Aurora forecasts and live maps can help you track potential sightings in the UK.
Tips for Photographing the Northern Lights
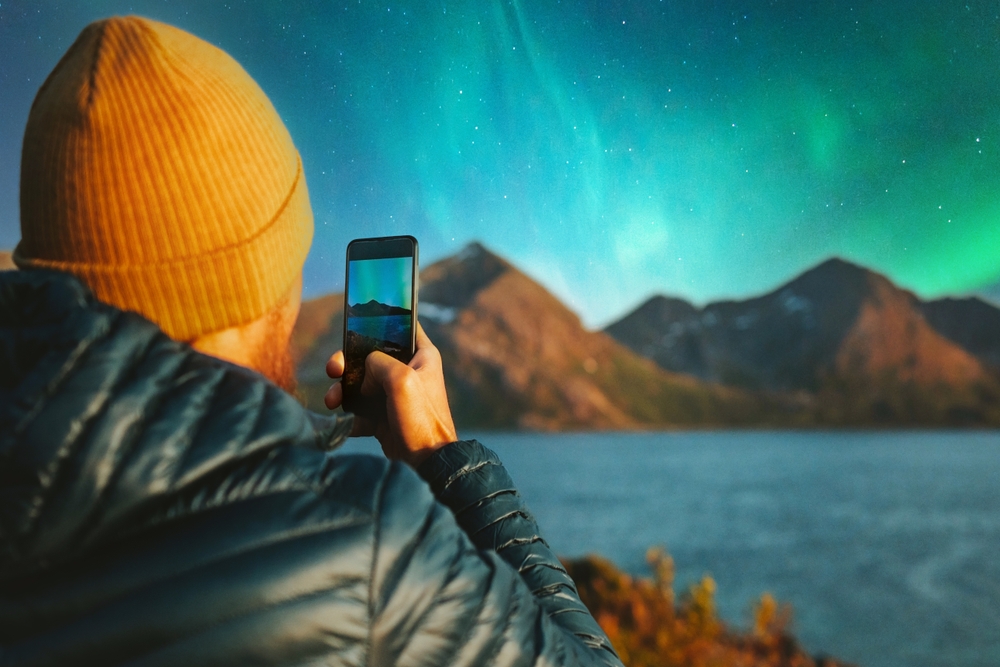

How to Photograph Northern Lights
Capturing the Northern Lights on camera requires some preparation and the right equipment. Here are a few tips:
- Use a tripod to keep your camera steady.
- Set your camera to a high ISO (800-3200).
- Use a wide-angle lens with a low aperture (f/2.8 or lower).
- Adjust your shutter speed to capture enough light (between 5 to 25 seconds).
- Manual focus on a distant light source.
Best Camera Settings for Northern Lights
To photograph the Northern Lights effectively, consider the following camera settings:
- ISO: 800-3200
- Aperture: f/2.8 or lower
- Shutter Speed: 5-25 seconds
- Focus: Manual, set to infinity or focus on a distant light
Taking great photos of the Northern Lights requires patience and practice. Always scout your location in daylight, dress warmly, and bring extra batteries as cold weather can drain them quickly. Experiment with different settings to find what works best for your conditions.
Northern Lights Forecasts and Tracking
Many websites and apps provide forecasts, helping you plan your viewing trip. These forecasts predict the likelihood of light activity based on solar wind conditions and geomagnetic activity.
Aurora Map and Northern Lights Maps
Aurora maps show where the Northern Lights are currently visible and forecasted to appear. They are valuable tools for aurora chasers, helping you decide where to go for the best viewing opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Northern Lights
Can you see the Northern Lights with the naked eye?
The Northern Lights can be seen with the naked eye. However, their visibility depends on various factors such as light pollution, weather conditions, and the intensity of the auroral activity. The lights often appear as a faint glow or a dancing curtain of colours in the night sky.
What is the difference between Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis?
Aurora Borealis refers to the Northern Lights, visible in the northern hemisphere around the Arctic region. Aurora Australis, on the other hand, is the Southern Lights, visible in the southern hemisphere around the Antarctic region. Both phenomena are caused by the same process of solar particles interacting with the Earth's magnetic field.
How often can you see the Northern Lights?
The frequency of seeing the Northern Lights varies depending on your location and the level of solar activity. In places within the auroral oval, such as northern Norway or Canada, the lights can be seen fairly regularly during the winter months. However, solar activity cycles every 11 years, meaning some years will have more frequent and intense displays than others.
Is there a specific time of night when the Northern Lights are most visible?
The Northern Lights are typically most visible between 10 PM and 2 AM local time. However, they can appear anytime during the night when the skies are dark and clear.
Can the Northern Lights be predicted accurately?
Aurora forecasts provide a good indication of when and where the Northern Lights might be visible based on solar wind data and geomagnetic activity. Websites and apps dedicated to aurora tracking can give you real-time updates and short-term predictions. However, these forecasts are not 100% accurate due to the unpredictable nature of space weather.
Do the Northern Lights make any sound?
While it is extremely rare, some people have reported hearing faint sounds during intense auroral displays. These sounds are described as crackling or rustling noises. Scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited, and the phenomenon remains a topic of debate among researchers.
Why are the Northern Lights more common in winter?
The Northern Lights are more common in winter because the nights are longer and darker, providing better viewing conditions. Additionally, winter weather often brings clearer skies in the high-latitude regions, which enhances visibility.
Can you see the Northern Lights from space?
Astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) and other spacecraft can see the Northern Lights from space. From their vantage point, the auroras appear as glowing rings encircling the poles, offering a unique and breathtaking perspective.
What are some myths and legends associated with the Northern Lights?
Throughout history, many cultures have created myths and legends about the Northern Lights. For example:
- In Norse mythology, the lights were believed to be the reflections of the Valkyries' armour as they led fallen warriors to Valhalla.
- Indigenous Sami people in Scandinavia believed the lights were the souls of their ancestors, and they held great spiritual significance.
- In Finnish folklore, the lights were thought to be caused by a magical fox sweeping its tail across the snow, creating sparks that lit up the sky.
Are there any health benefits to watching the Northern Lights?
While there are no direct health benefits linked to watching the Northern Lights, the experience can have positive effects on mental well-being. The beauty and awe-inspiring nature of the lights can evoke feelings of wonder and joy, reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
What should I wear when going to see the Northern Lights?
When planning to view the Northern Lights, especially in winter, it's essential to dress warmly. Wear multiple layers, including thermal undergarments, a heavy coat, gloves, a hat, and warm boots. Consider bringing hand warmers and a blanket, as you might be standing outside in cold conditions for an extended period.
Recommended for you!
Best SellersStudy Cosmology for £29
If you are intrigued by the wonders of the cosmos and want to learn more about the mysteries of the universe, consider enrolling in the Cosmology Diploma Course with Centre of Excellence. For a limited time, the course is available for a discounted price of £29.