Among the many constellations that decorate the sky, Vela is a lesser-known yet captivating one that offers intriguing stories and scientific marvels. If you're curious about the constellation Vela, whether for stargazing, astrology, or just for fun, this guide shares its history, appearance, and remarkable features.
Jump to:
Recommended for you!
Best SellersWhat is the Vela Constellation?
The Vela constellation is one of the 88 officially recognised constellations and is located in the Southern Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word for "sails," as it represents the sails of the mythical ship Argo Navis from ancient Greek mythology. In the 18th century, Argo Navis, a massive constellation representing the entire ship, was divided into smaller parts: Vela (the sails), Carina (the keel), and Puppis (the stern). Today, Vela stands as a separate constellation, yet it remains closely linked to its original maritime heritage.
What Does Vela Look Like?
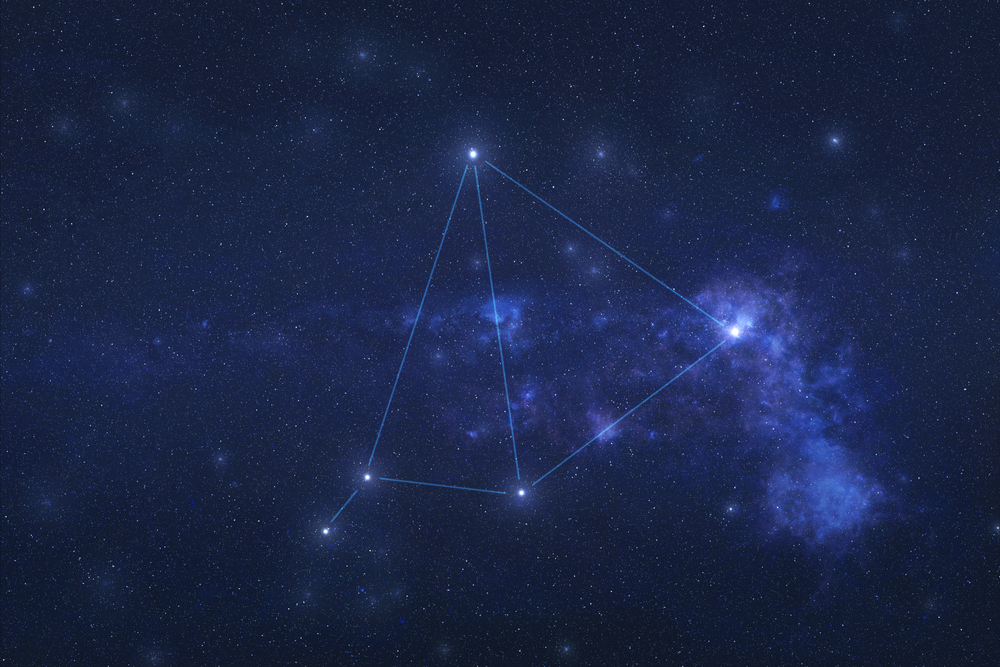

Vela is not one of the most recognisable constellations, but it does contain a number of bright stars that make it easier to spot in the sky. The constellation resembles a series of sail-like shapes when the main stars are connected, hinting at its nautical origin. Vela does not have any single, defining shape like some more famous constellations (e.g., Orion's "belt"), but its collection of stars forms a somewhat sprawling pattern that suggests the flowing sails of a ship.
How Far is the Vela Constellation from Earth?
The Vela constellation is situated within our Milky Way galaxy, which means its stars are relatively nearby in cosmic terms. The individual stars within Vela are at different distances from Earth, with some being hundreds of light-years away. The constellation itself does not have a set distance from Earth because it is made up of multiple stars, each at a different point in space. However, one of its notable features, the Vela Supernova Remnant, is approximately 800 light-years away. This remnant, a cloud of debris left over from a star that exploded about 11,000 years ago, is one of the closest supernova remnants to our planet.
The Vela Constellation Myth
The mythology behind Vela connects it to the story of Jason and the Argonauts, a famous Greek myth. The ship Argo was said to have been built by the master craftsman Argus under the guidance of the goddess Athena. It carried Jason and his crew on their quest to find the Golden Fleece, encountering numerous adventures along the way. When the constellation Argo Navis was later split into three parts, Vela inherited the connection to the sails of this legendary ship.
Vela's Stars

Vela contains many stars, some of which are brighter and more prominent than others. Here are a few of the key stars that make up this constellation:
- Gamma Velorum (Regor): This is the brightest star in Vela and actually a complex system of multiple stars. It appears as a bright, bluish star in the sky, located about 336 light-years from Earth. One of its components is a rare type of star known as a Wolf-Rayet star, which is in a later stage of stellar evolution.
- Delta Velorum: This star is also a binary system, consisting of two stars orbiting each other. It's visible to the naked eye and appears bright in the night sky.
- Kappa Velorum (Markeb): Another notable star, Kappa Velorum is part of the group of stars that form the shape of the sails. It shines brightly and serves as a useful reference point for locating the constellation.
Nebulae in the Vela Constellation
One of the most fascinating aspects of Vela is the presence of nebulae and other deep-sky objects that make this region of space particularly interesting for astronomers:
- The Vela Supernova Remnant: This nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust formed from the remnants of a massive star that exploded in a supernova. It is an extensive structure with intricate filaments that can be observed through telescopes. The remnant continues to expand, and the shockwaves from the explosion are still moving through the surrounding space, creating stunning visual effects.
- The Gum Nebula: Although only part of this enormous nebula lies within Vela, it is worth mentioning due to its sheer size. The Gum Nebula is one of the largest known emission nebulae, stretching across a significant portion of the southern sky. It is believed to be the result of several supernovae that occurred millions of years ago.
Finding Vela in the Sky

To catch a good view of the Vela constellation, aim to stargaze during the southern autumn months, especially from February to April. During this period, Vela reaches its highest point in the sky, making it more visible and easier to spot.
Locating Vela
Begin by identifying the nearby constellations of Carina and Puppis, which are more prominent in the southern sky. These constellations were once part of the larger Argo Navis, along with Vela. By locating Carina or Puppis first, you’ll have a better chance of finding Vela nearby, completing the trio. The sails of Vela extend to the east of Carina and to the south of Puppis.
For greater accuracy, consider using a star map or a stargazing app. These tools will help you pinpoint the stars of Vela in the current night sky, particularly since some of its stars may not be as bright as those in neighbouring constellations.
Viewing Vela with Binoculars or a Telescope
- With Binoculars: Although Vela’s stars may appear faint to the naked eye, binoculars can help you trace the constellation’s shape and better appreciate its unique features.
- With a Telescope: A telescope provides a clearer and more detailed view of Vela’s stars and its remarkable deep-sky objects, such as the Vela Supernova Remnant. Focusing on brighter stars, like Gamma Velorum, will enhance your understanding of Vela’s structure.
Best Viewing Conditions
To fully enjoy Vela, choose a location with minimal light pollution and a clear, dark sky, preferably on a moonless night. These conditions will maximise your chances of observing Vela’s subtle star patterns and its fascinating nebulae.
Recommended for you!
Best SellersFun Facts About Vela
- Part of the Milky Way: Vela is situated within the Milky Way, and its stars, nebulae, and supernova remnants contribute to the bright band of light that stretches across the sky.
- Home to a Pulsar: The Vela Pulsar is a highly magnetised, rotating neutron star that emits beams of radiation. It is one of the most studied pulsars due to its relatively close proximity to Earth.
- A Source of Gamma Rays: The Vela Supernova Remnant is known to emit gamma rays, making it a significant object of interest for scientists studying cosmic radiation.
Study Astronomy for £29
If you’ve enjoyed this guide to the Vela constellation and want to learn more about the stars, nebulae, and other wonders of the universe, consider studying astronomy in greater depth. Centre of Excellence offers an Astronomy Diploma Course that provides a fascinating introduction to stargazing, celestial objects, and the science behind the night sky. The course is currently available for just £29!