One of the lesser-known but fascinating constellations is Triangulum, a small yet distinctive constellation with a triangular shape that makes it easy to identify once you know where to look. This guide shares everything you need to know about Triangulum, from its history and mythology to the stars and galaxies within it.
Jump to:
- What is the Triangulum Constellation?
- What Does Triangulum Look Like?
- How Far is the Triangulum Constellation from Earth?
- The Triangulum Constellation Myth
- Triangulum’s Stars
- Nebulae and Galaxies in the Triangulum Constellation
- Finding Triangulum in the Sky
- Fun Facts About Triangulum
- Study Astronomy for £29
Recommended for you!
Best SellersWhat is the Triangulum Constellation?
The Triangulum constellation, named for its triangular shape, is one of the 88 official constellations recognised today. While not as famous as Orion or the Big Dipper, Triangulum is easy to locate due to its simple shape, which resembles a small triangle in the night sky.
The Meaning of Triangulum
The word "Triangulum" is Latin for "triangle," a fitting name for this constellation due to its distinct three-star structure.
What Does Triangulum Look Like?
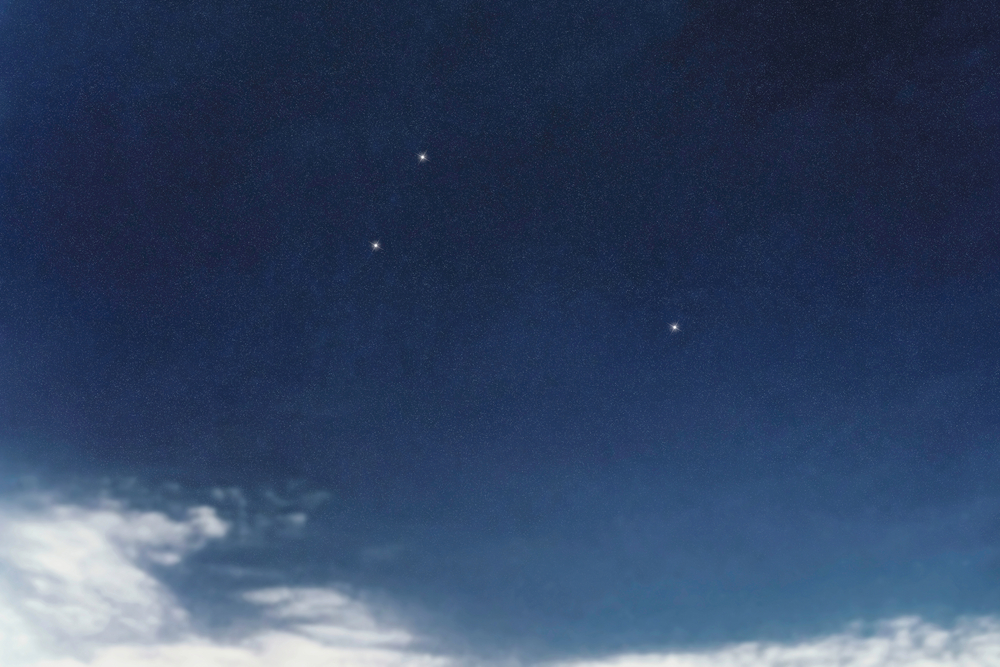

Triangulum consists of three primary stars, forming a simple but distinct triangle. It’s not particularly large or bright compared to other constellations, so you may need a clear, dark sky to spot it. The constellation is visible to the naked eye, though it may be easier to observe if you’re in a place with minimal light pollution.
How Far is the Triangulum Constellation from Earth?
Triangulum itself is not measured by a specific distance from Earth because it’s composed of various stars, each at different distances from our planet. The closest of its stars is relatively nearby, but it’s the Triangulum Galaxy that stands out, lying about 3 million light-years away. This galaxy is one of the closest large galaxies to Earth and provides a fascinating focal point for astronomers.
The Triangulum Constellation Myth

Ancient cultures often attributed myths and stories to constellations, and Triangulum is no exception. In Greek mythology, this constellation represented the fertile Nile Delta, symbolising growth and sustenance. The triangular shape was thought to resemble the Nile Delta itself, a crucial part of ancient Egypt. Other cultures associated it with symbolic shapes, often triangles, due to its straightforward structure.
Triangulum’s Stars
While it may be a small constellation, Triangulum contains a few notable stars:
- Beta Trianguli – The brightest star in the constellation, this white giant is located about 127 light-years away from Earth. It forms one of the points in the triangle.
- Gamma Trianguli – A smaller, hotter star, Gamma Trianguli is another significant component of the constellation and lies around 118 light-years from Earth.
- Alpha Trianguli – This star completes the triangle shape and is located around 63 light-years away.
Nebulae and Galaxies in the Triangulum Constellation
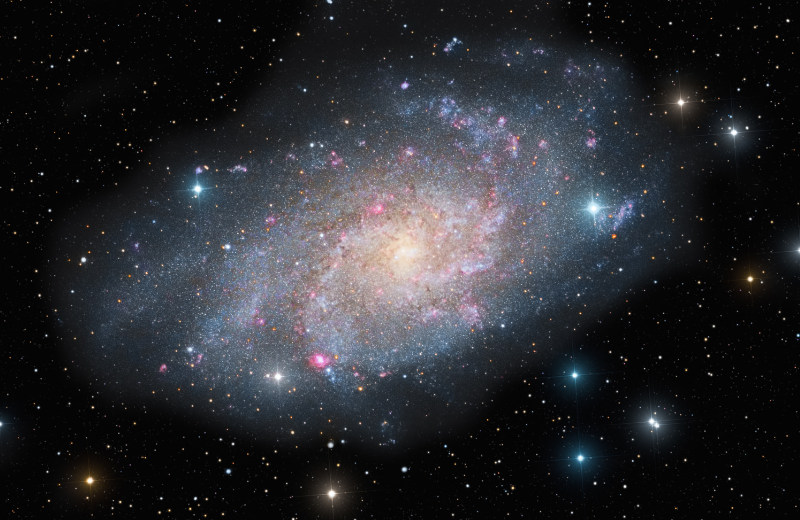

One of the highlights within the Triangulum constellation is the Triangulum Galaxy (M33). Known for its spiral shape, this galaxy is the third largest in our Local Group of galaxies, after the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way. Located around 3 million light-years away, the Triangulum Galaxy is often a target of study for astronomers because of its proximity and visibility.
What Makes the Triangulum Galaxy Special?
The Triangulum Galaxy is notable not only for its proximity but also for its beauty and structure. It has a well-defined spiral shape and is home to several star-forming regions, making it a rich field of study for those interested in the birth of stars. Some astronomers have suggested that it may contain a small black hole, though this is still under investigation.
Interestingly, while larger telescopes provide the best views, you may be able to spot the Triangulum Galaxy with a good pair of binoculars or a small telescope under dark-sky conditions.
Finding Triangulum in the Sky
Triangulum is best viewed during the autumn and winter months in the Northern Hemisphere, with the clearest visibility occurring from November to February. During this period, Triangulum reaches its highest point in the sky, making it easier to locate in the evening hours.
Locating Triangulum
To locate Triangulum, start by identifying the constellation of Andromeda, a prominent feature in the northern sky. Triangulum lies close to Andromeda and forms a distinctive triangular shape. A star map or astronomy app can also help you pinpoint this modest yet intriguing constellation with greater accuracy.
Viewing Triangulum with Binoculars or a Telescope
- Using binoculars: While the primary stars of Triangulum can be seen with the naked eye under dark conditions, binoculars allow you to pick up on some of the fainter stars, enhancing the constellation’s triangular form.
- Using a telescope: With a telescope, you can observe the Triangulum Galaxy (M33), one of the closest galaxies to Earth. This spiral galaxy offers an exciting opportunity to see a distant galaxy and get a closer view of one of our galactic neighbours.
Best Viewing Conditions
For the best viewing experience, find a location with minimal light pollution on a clear, moonless night. Under dark skies, Triangulum becomes more visible, and the stars defining its triangular shape come into clearer focus. If you’ve already spotted Andromeda, Triangulum will be close by, providing an exciting chance to explore this unique part of the sky.
Recommended for you!
Best SellersFun Facts About Triangulum
- Triangulum Galaxy’s Real Name – The Triangulum Galaxy is also known as M33, part of the Messier catalogue, a famous listing of astronomical objects.
- Not Part of the Milky Way – Although we often observe it from within our galaxy, the Triangulum Galaxy is its own separate entity and one of the closest galaxies to the Milky Way.
- Future of the Triangulum Galaxy – It is speculated that the Triangulum Galaxy may eventually collide with the Andromeda Galaxy and, possibly, the Milky Way in a distant cosmic event.
- Planetary Possibilities – While it’s challenging to observe individual planets within the Triangulum Galaxy, astronomers believe there may be planets orbiting its stars.
- Visibility Without a Telescope – Under optimal conditions, the Triangulum Galaxy is visible to the naked eye, making it one of the most distant objects that can be seen without any equipment.
Study Astronomy for £29
If the Triangulum constellation has sparked your curiosity, why not explore more about the stars and the cosmos with our Astronomy Diploma Course at Centre of Excellence? This course offers a detailed understanding of the universe, from constellations and star types to the fundamentals of space observation. Perfect for all budding astronomers, the course is available for a discounted price of £29.