The Reticulum constellation is a lesser-known but captivating area to explore. Whether you’re just starting your astronomical journey or already have some knowledge, this guide shares everything you need to know about Reticulum, from its appearance and distance from Earth to its mythological background and unique stars.
Jump to:
What is the Reticulum Constellation?
Reticulum is a small constellation located in the southern hemisphere. The name "Reticulum" means "the net" in Latin, a reference to the small net-like pattern it forms in the night sky. It was named after the reticle, a crosshair used in telescopes and other optical instruments, highlighting its connection to astronomy and navigation.
Reticulum might not be as well-known as other constellations like Orion or Cassiopeia, but its modest size and unique shape make it a fascinating subject for stargazers interested in the less-explored parts of the sky.
Recommended for you!
Best SellersWhat Does Reticulum Look Like?
Reticulum is a faint constellation that requires clear, dark skies to observe. It doesn’t boast the bright stars that make other constellations instantly recognisable, but its distinctive pattern can be seen with a good telescope or even binoculars. The constellation consists of a few stars arranged in a net-like formation, living up to its name.
How Far is the Reticulum Constellation from Earth?
The Reticulum constellation is located within the Milky Way galaxy, like many other constellations visible to us from Earth. However, the distance of its stars varies. The constellation itself is not a single entity with one fixed distance; instead, it is made up of multiple stars at various distances.
For example, some of Reticulum’s stars are situated hundreds of light-years away, while others may be much closer.
The Reticulum Constellation Myth
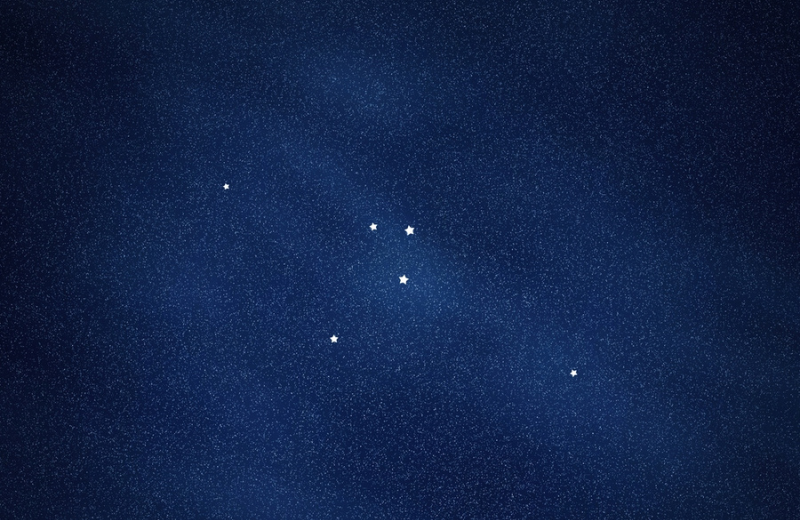

Unlike many other constellations that are tied to ancient Greek or Roman myths, Reticulum does not have a mythological story. It was named in the 18th century by the French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille. Lacaille mapped out several constellations in the southern sky that had previously been uncharted, and he named Reticulum after the reticle in the eyepiece of his telescope.
This practical and modern origin sets Reticulum apart from constellations with mythical stories, showing that not all constellations are steeped in legend—some have their roots in the development of scientific tools and methods.
Reticulum's Stars
Although Reticulum is a faint constellation, it is home to some interesting stars:
- Alpha Reticuli: The brightest star in the constellation, Alpha Reticuli is a giant star located about 162 light-years from Earth. It has a magnitude of 3.3, making it visible to the naked eye under good conditions.
- Beta Reticuli: This star is a bit dimmer, with a magnitude of 3.8. It is also located relatively close to Earth at about 100 light-years away. Beta Reticuli adds to the net-like pattern that characterises the constellation.
Nebulae in the Reticulum Constellation
Reticulum is not known for hosting any famous nebulae; however, its location in the southern sky still offers a good view of nearby star clusters and other celestial phenomena. With a powerful telescope, you may spot faint clouds of interstellar gas and dust that contribute to the overall beauty of the Milky Way galaxy.
Finding Reticulum in the Sky

To observe Reticulum at its best, aim to stargaze during the southern summer months, particularly from December to January, when the constellation reaches its highest point, making it more visible in the night sky.
Locating Reticulum
To locate Reticulum, begin by identifying its neighbouring constellation, Dorado. Dorado is well-known for containing part of the Large Magellanic Cloud, a neighbouring galaxy visible to the naked eye. By pinpointing Dorado first, you can then navigate to the nearby position of Reticulum.
For a more precise view, using a star map or a stargazing app can greatly assist in pinpointing Reticulum’s location in the night sky. These tools align with the current night sky, guiding you to the faint stars that form the Reticulum constellation.
Viewing Reticulum with Binoculars or a Telescope
- With Binoculars: While Reticulum’s stars are faint, binoculars can help you enhance their visibility, allowing you to trace the delicate net-like pattern of the constellation.
- With a Telescope: A telescope provides a more detailed and clearer look, especially when focusing on its brightest stars, such as Alpha Reticuli and Beta Reticuli. This can offer a better appreciation of the constellation's structure.
Best Viewing Conditions
For the optimal viewing experience, choose a location with minimal light pollution and a clear, dark sky, preferably on a moonless night. These conditions will give you the best chance to appreciate Reticulum and its subtle stars fully.
Fun Facts About Reticulum
- Reticulum’s Size and Position: Reticulum is one of the smaller constellations in the sky, covering an area of approximately 114 square degrees. It is bordered by the constellations Dorado and Hydrus, making it a distinct feature in the southern hemisphere.
- Modern Origins: Reticulum is a relatively recent addition to the constellation map, first catalogued in the 18th century by the French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille. Its modern origin highlights its connection to advancements in astronomy during that period.
- Telescope Inspiration: The name "Reticulum" reflects its use in telescope technology, specifically referring to the reticle or crosshair used in the eyepiece of telescopes. This demonstrates the close relationship between astronomical tools and the naming of constellations.
- Home to Binary Stars: Reticulum includes several binary star systems, such as Zeta Reticuli. This system, consisting of two stars orbiting each other, provides astronomers with a fascinating subject for studying stellar motion and dynamics.
Recommended for you!
Best SellersStudy Astronomy for £29
If the Reticulum constellation has sparked your curiosity, why not explore more about the stars and the cosmos with our Astronomy Diploma Course at Centre of Excellence? This course offers you a detailed understanding of the universe, from constellations and star types to the fundamentals of space observation. Perfect for all budding astronomers, the course is available for a discounted price of £29.