When you gaze up at the night sky, especially during the winter months, there’s a good chance you’ll spot one of the most famous constellations: Orion. Its distinctive pattern is easily recognisable by the three bright stars that form Orion's Belt. Whether you're a seasoned stargazer or simply curious about the stories written in the stars, Orion offers something for everyone. This article guides you through the key facts about Orion's constellation, its stars, and the rich mythology behind it.
Jump to:
Recommended for you!
Best SellersWhat is the Orion Constellation?
Orion is one of the most prominent and easily recognisable constellations in the night sky. Named after a mighty hunter from Greek mythology, Orion is visible from almost every part of the world. It is most noticeable during the winter months in the Northern Hemisphere, making it a familiar sight for stargazers.
What Does Orion Look Like?
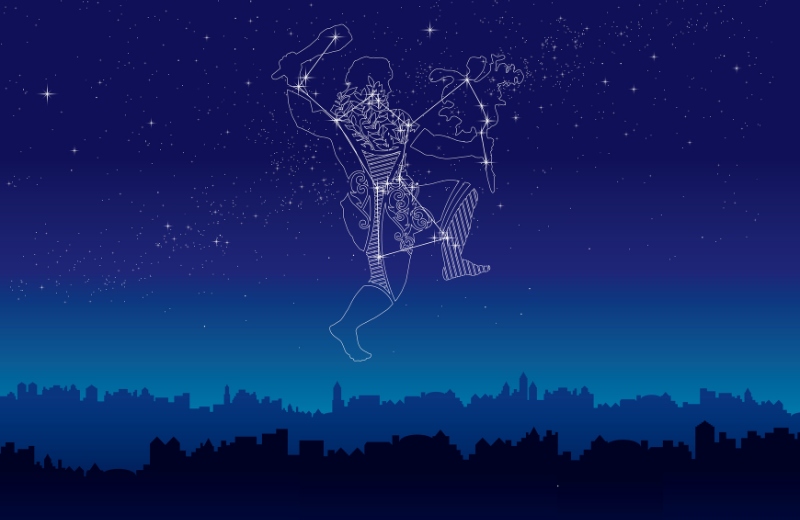

Orion’s constellation is easy to identify due to its distinctive shape. The most striking feature is Orion's Belt, consisting of three bright stars—Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka—arranged in a straight line. Above the Belt, you’ll find two stars marking Orion’s shoulders: Betelgeuse and Bellatrix. Below the Belt, Rigel and Saiph represent his legs. This arrangement gives Orion the appearance of a hunter standing tall in the sky, often depicted with a bow or club raised above his head.
The Orion Constellation Myths
The constellation of Orion is steeped in mythology. In Greek mythology, Orion was a mighty hunter, the son of Poseidon, the god of the sea. Stories about Orion vary, but he is often depicted as a giant who could walk on water, thanks to his divine parentage.
The Tragic Tale of Orion
One of the most famous myths surrounding Orion involves his tragic death. According to legend, Orion boasted that he could hunt and kill every animal on Earth. This angered the goddess Artemis or Gaia (depending on the version), who sent a giant scorpion to slay him. Orion was stung by the scorpion and died, but Zeus placed him among the stars to honour his hunting prowess. The Scorpius constellation, representing the scorpion, was also placed in the sky, but far from Orion, so the two would never be seen at the same time.
Orion’s Belt and the Pyramids of Giza
There’s also a fascinating connection between Orion’s Belt and the pyramids of Giza in Egypt. Some researchers believe that the three pyramids were constructed to align with the three stars of Orion’s Belt, reflecting the Egyptians' deep connection to the stars and their beliefs in the afterlife.
What Does the Orion Constellation Symbolise?

The Orion constellation is often seen as a symbol of strength, courage, and the warrior spirit. In various cultures, it has been associated with different myths and spiritual meanings. In ancient Egypt, Orion was linked to Osiris, the god of the afterlife, and the constellation was believed to guide the souls of the dead. In modern times, Orion’s Belt is sometimes viewed as a bridge between the physical and spiritual worlds, representing balance and unity.
What Galaxy is Orion In?
Orion is within our Milky Way galaxy. The stars that make up the Orion constellation are all part of the Milky Way, which is the galaxy that contains our Solar System. Although the stars in Orion appear close together from our perspective on Earth, they are actually vast distances apart from each other and from us.
How to Pronounce Orion
The correct pronunciation of Orion is "Oh-RYE-un." The name comes from Greek mythology and has been used for centuries to describe this iconic constellation. It’s important to stress the second syllable, "RYE," to pronounce it correctly.
Orion’s Stars
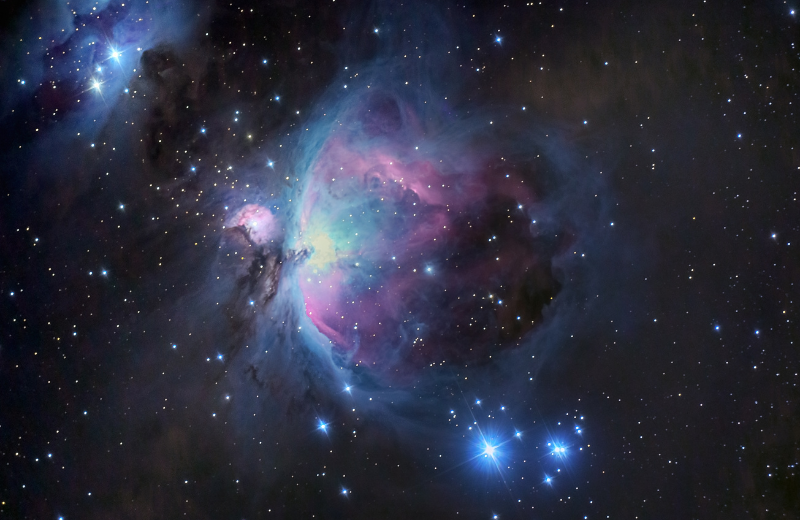

Orion’s constellation is home to several of the brightest and most famous stars in the night sky. Here are some of the key stars that make up this iconic constellation:
Betelgeuse: The Red Giant
Betelgeuse is perhaps the most famous star in Orion and one of the brightest in the sky. This red supergiant marks the hunter’s left shoulder and is notable for its reddish hue. Betelgeuse is nearing the end of its life and is expected to explode as a supernova at some point in the next million years, an event that will be visible from Earth.
Rigel: The Blue-White Supergiant
Rigel, located at Orion’s left foot, is another extremely bright star, often considered the brightest star in Orion's constellation. It is a blue-white supergiant, much hotter and more massive than our Sun. Rigel’s brightness makes it a significant point of interest for astronomers.
Bellatrix: The Female Warrior
Bellatrix, marking Orion’s right shoulder, is a blue giant star. Its name means "female warrior," and it shines brightly in the sky, although not as prominently as Betelgeuse or Rigel. Bellatrix is often associated with courage and strength.
Orion's Belt: Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka
The three stars that make up Orion’s Belt are some of the most recognisable in the entire night sky. Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka are all massive, hot stars that shine brightly, making the Belt easy to spot even in light-polluted areas. These stars are nearly equidistant from each other, forming a straight line that is instantly recognisable.
Saiph: The Brightest Star You May Not Notice
Saiph, though not as well-known as Betelgeuse or Rigel, is another bright star in Orion, marking the hunter’s right knee. Like Rigel, Saiph is a blue-white supergiant, but it often goes unnoticed because of the brilliance of its neighbours.
Nebulae in Orion Constellation
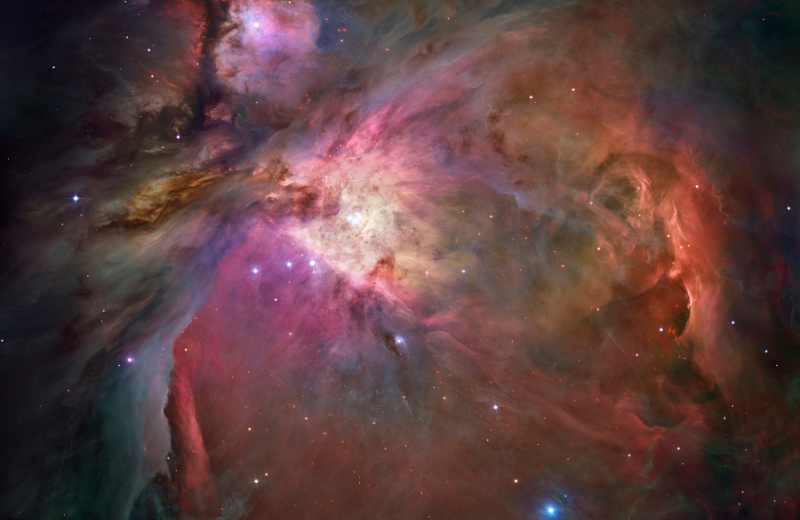

Orion is also home to some spectacular nebulae, vast clouds of gas and dust where new stars are born.
The Orion Nebula (M42)
The Orion Nebula is one of the brightest nebulae in the sky and can be seen with the naked eye. Located below Orion's Belt, this diffuse nebula is a stellar nursery where new stars are forming. It’s a popular target for amateur astronomers because it offers a stunning view even through small telescopes.
The Horsehead Nebula
Near Alnitak, one of the stars in Orion’s Belt, lies the Horsehead Nebula. This dark nebula gets its name from its horsehead-like shape, which stands out against the glowing backdrop of ionised hydrogen. While it’s more challenging to spot than the Orion Nebula, it’s a favourite among astrophotographers.
Finding Orion in the Sky
Orion is most easily seen during the winter months in the Northern Hemisphere. To find it, look towards the southern sky in the evening. The three stars of Orion’s Belt make the constellation easy to spot, even in areas with light pollution. In the Southern Hemisphere, Orion appears in the northern sky, but it is upside down compared to how it is viewed from the Northern Hemisphere.
The Best Time and Place to See Orion
If you’re eager to see Orion in all its glory, the best time to look is during the winter months. In the Northern Hemisphere, December through March are ideal. The best views are away from city lights, where the full brilliance of the constellation can be appreciated. Orion rises in the east and sets in the west, making it visible for much of the night.
Recommended for you!
Best SellersWhat Is the Spiritual Meaning of Orion?
For many cultures, Orion has spiritual significance. In Egyptian Mythology, Orion was associated with Osiris, the god of the afterlife, and was believed to be a guide for the souls of the dead. The constellation’s appearance in the sky was seen as a symbol of renewal and rebirth.
Orion in Astrology and Symbolism
Though Orion is not a part of the zodiac, its symbolism is still powerful. The constellation is often seen as a representation of strength, courage, and the warrior spirit. Some people feel a deep connection to Orion, finding in its stars a source of inspiration and a reminder of the vastness of the universe.
What Does Orion's Belt Mean Spiritually?
Orion’s Belt, with its three aligned stars, is often seen as a gateway or a bridge between the physical and spiritual worlds. In various spiritual traditions, it represents balance, unity, and the journey towards enlightenment.
Fun Facts About Orion
- Betelgeuse: Betelgeuse is expected to explode as a supernova sometime in the next million years, an event that will be visible from Earth.
- Orion’s Belt and the Pyramids: The three pyramids of Giza are thought to be aligned with the stars of Orion’s Belt, reflecting the ancient Egyptians’ worship of the stars.
- Visible From Most of the World: Orion is one of the few constellations that can be seen from almost every part of the world.
- Spiritual Significance: In some cultures, Orion is believed to be a gateway between the physical and spiritual realms.
Study Astronomy for £29
If you’re fascinated by the stars and want to learn more about the universe, consider enrolling in our Astronomy Diploma Course at Centre of Excellence. You’ll gain a detailed understanding of the stars, planets, and celestial phenomena, all from the comfort of your own home. Sign up today for a discounted price of £29 and start your journey into the cosmos!