Did you know that Cupid, the famous symbol of love, originally had his roots in Roman mythology? What’s more, there's more to this god of love than first meets the eye. His story is filled with symbolism, dramatic mythological tales, and a surprising amount of depth.
Whether you’re curious about the story of Cupid and Psyche, interested in learning more about what Cupid symbolises, or simply fascinated by Roman gods, this guide helps you understand the many layers of Cupid’s character.
Jump to:
- Who Was Cupid in Roman Mythology?
- Cupid’s Myths
- The Role of Cupid in Roman Storytelling
- What Powers Did Cupid Possess?
- Symbols Associated with Cupid
- Cupid’s Lineage and Connections
- Why Is Cupid Special?
- Cupid in Modern Culture
- Cupid’s Worship and Legacy
- Frequently Asked Questions About the Goddess Cupid
- Study Roman Mythology for £29
Recommended for you!
Best SellersWho Was Cupid in Roman Mythology?
Cupid is the Roman god of love, known for sparking desire and affection in both mortals and gods. In Latin, his name means “desire,” which gives a strong clue about his role in Roman mythology. Often portrayed as a winged infant or young boy, he carries a bow and arrows that can cause people to fall hopelessly in love.
Though you might associate Cupid with romantic love today, his powers extended beyond hearts and roses. In mythology, he was a divine force capable of stirring passion, chaos, temptation, and longing. His figure has inspired everything from statues to poetry and art, and his influence remains widespread even now.
Cupid’s Myths
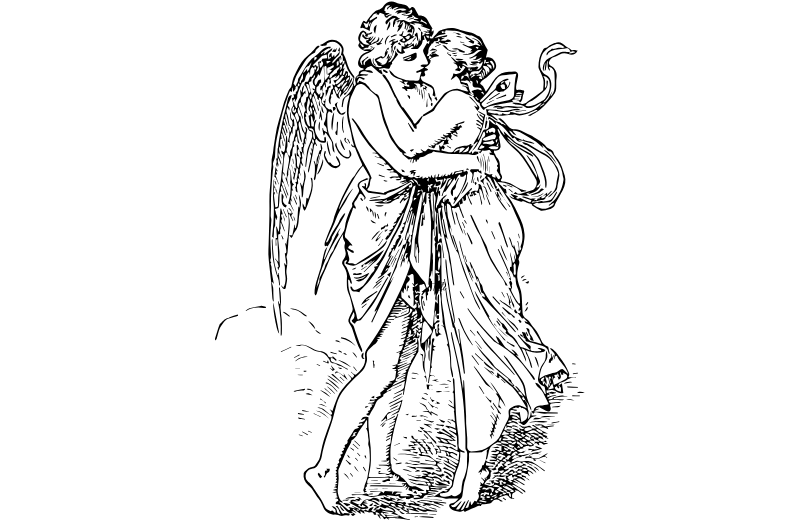
Cupid features in several myths, but none are as well-known or emotionally rich as those involving Psyche. These stories reveal different aspects of love—its joy, challenges, and power to transform.
The Story of Cupid and Psyche
The most famous tale involving Cupid is the story of Cupid and Psyche, a romantic and deeply symbolic myth that has been retold for centuries. Cupid falls in love with Psyche, a mortal woman of extraordinary beauty, but their love is tested by secrets, separation, and divine challenges.
Psyche is taken to a magical palace where she is cared for by an unseen husband—Cupid in disguise. When she breaks the rule never to look at him, he flees, and she must prove her love through a series of difficult tasks. After many trials, including a journey to the underworld, Psyche’s devotion is rewarded. The gods grant her immortality so she and Cupid can be together forever. This myth highlights the idea that true love must be built on trust, patience, and resilience.
Psyche’s Trials and Venus’s Wrath
A deeper layer of the myth focuses on Psyche’s trials, set by Venus, Cupid’s mother, who’s jealous of Psyche’s beauty. Venus sees her as a rival and attempts to sabotage the relationship by giving her impossible tasks to complete.
These include sorting a mountain of mixed seeds, retrieving golden wool from dangerous sheep, and venturing into the underworld to collect a jar of beauty from Persephone. With help from supernatural allies and her own determination, Psyche succeeds. This part of the story shows how love is often tested and how inner strength is necessary to overcome obstacles.
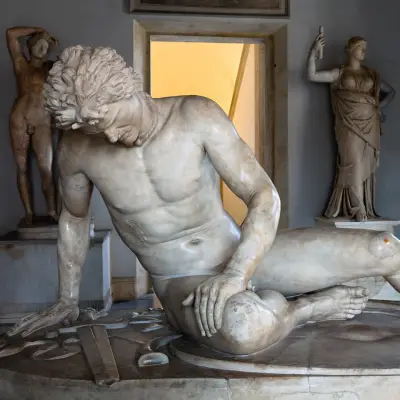
Psyche Revived by Cupid’s Kiss
The emotional climax of the myth comes when Psyche, having opened the jar from the underworld, falls into a deathlike sleep. Cupid, deeply in love, finds her and awakens her with a kiss.
This moment is beautifully captured in the famous sculpture Psyche Revived by Cupid’s Kiss, also referred to as Psyche Awakened by Cupid’s Kiss. It symbolises love’s power to heal, restore, and transcend even death—a theme that has echoed through art and literature for centuries.
The Role of Cupid in Roman Storytelling

Cupid plays many roles in Roman storytelling. He can be a matchmaker, a mischief-maker, and even a cautionary figure. He often appears in myths where love creates unexpected consequences—sometimes joyful, sometimes painful. His arrows do not distinguish between gods and mortals, making him a powerful, unpredictable figure in Roman mythology.
Cupid’s presence in myths reminds us that love is a force beyond control—it can be uplifting or destructive, irrational or transformative. He represents love in all its forms: romantic, impulsive, enduring, and flawed.
What Powers Did Cupid Possess?
Cupid’s main power is the ability to make people fall in love. His bow and arrows are magical. He carries two types: golden arrows that cause intense desire, and lead arrows that repel affection.
His supernatural gifts make him both enchanting and dangerous. Think of his arrows as metaphors for the sudden, often uncontrollable onset of love. People pierced by his arrows feel overwhelming emotions, sometimes for people they’ve just met.
His powers also made him a symbol of fate. Unlike other gods who relied on strength or war, Cupid wielded influence over emotions and hearts, making him powerful in a unique way.
Symbols Associated with Cupid
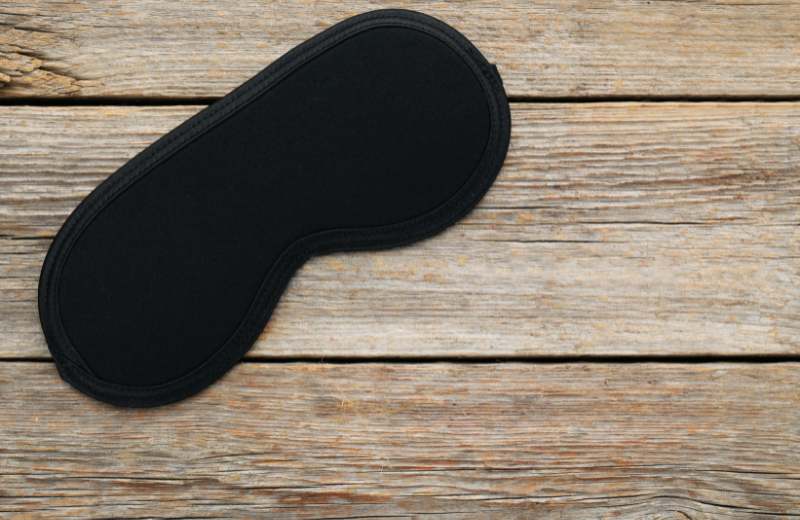

So, what does a Cupid symbolise? In art and literature, Cupid often represents passionate love, romantic desire, and the unpredictability of affection. He is commonly shown with:
- Wings, symbolising the fleeting nature of love
- Blindfold, representing love’s blindness
- Bow and arrows, denoting how quickly love can strike
- Flames, showing the intensity of emotion
What Is the Meaning of Cupid’s Arrow?
Cupid’s arrow is more than just a romantic trope—it’s a metaphor for the sudden and often unexplainable feeling of falling in love. In myth, his golden arrows inspire desire, while his leaden arrows create aversion. Spiritually and symbolically, they represent how love can be both beautiful and painful, depending on the nature of the connection.
Cupid’s Lineage and Connections
Cupid’s parents are two of the most important figures in Roman mythology. His mother is Venus, the goddess of love and beauty, and their close relationship is significant. In the myth of Cupid and Psyche, Venus becomes a key antagonist, which adds another layer to the story.
Cupid's father, depending on the myth, is often said to be Mars, the god of war. This pairing of love and war creates a fascinating contrast, showing the complexity of Cupid’s character.
Why Is Cupid Special?
Cupid stands out among Roman gods because of his deep connection to emotion. He’s more than just a mischievous matchmaker. His stories reveal powerful truths about love: it can’t be forced, it must be earned, and it often comes with challenges.
Cupid in Modern Culture

Today, Cupid shows up everywhere—from greeting cards to Cupid tattoos, films, and Valentine’s Day decorations. Cupid tattoos usually symbolise love, romance, and the hopeful or playful side of passion. Sometimes, they can also represent a personal story of emotional connection or heartache.
Cupid has become so well-known that he's almost a pop culture figure, but his origins remain rooted in myth and symbolism. He has appeared in countless forms of media, from cartoons and romantic comedies to literature and advertising.
In Disney’s Hercules, a Cupid-like figure makes a brief appearance, reinforcing the connection between gods and mortal emotions. He features prominently in Shakespeare’s plays—particularly A Midsummer Night’s Dream, where love is manipulated in ways reminiscent of Cupid’s arrows.
In more modern examples, Cupid is referenced in romantic films like Valentine’s Day, where his name and imagery play into the themes of love and relationships. Even in animated series like The Simpsons, Cupid appears as a comedic, mischievous character, bringing love—sometimes unwanted—to unsuspecting people.
Cupid has also inspired art for centuries. In the visual arts, especially Renaissance works, Cupid often appears in romantic scenes or as part of Cupid and Psyche sculpture.
Cupid’s Worship and Legacy
In ancient times, Cupid wasn’t just a decorative figure—he was worshipped in temples and revered in stories. Though he wasn’t one of the most powerful gods, his impact was deeply felt. His legacy lived on in Roman poetry, especially through writers like Ovid, who detailed the history of Cupid and his love stories.
Recommended for you!
Best SellersFrequently Asked Questions About Cupid
What is the meaning of Cupid?
Cupid symbolises romantic desire, often sudden and powerful. He represents the unpredictable and overwhelming nature of attraction that can strike at any moment.
Is Cupid the personification of love?
Yes, in many ways. He embodies both the joy and complexity of love, acting as a symbol of affection, passion, and emotional vulnerability.
What does Cupid control?
Emotion, desire, attraction—essentially, the heart. Through his arrows, he influences feelings and connections between individuals, regardless of their will.
Why is Cupid portrayed as a baby?
Cupid’s childlike form symbolises innocence and the unpredictable nature of love. It reminds us that love can come unexpectedly and affect us in ways we don’t always understand.
What is the curse of Cupid?
In some versions of his myth, love is a burden, especially when it causes chaos or pain. Cupid’s own experiences—such as the trials faced with Psyche—show that even the god of love is not immune to heartache.
What do Cupid and Psyche symbolise?
Together, Cupid and Psyche represent the union of love and the soul. Their journey shows that love often requires growth, perseverance, and deep emotional insight.
What does a Cupid tattoo symbolise?
A Cupid tattoo usually symbolises love, romantic longing, or a reminder of a powerful emotional experience. It can also reflect a playful or idealistic view of relationships.
What does playing Cupid mean?
Playing Cupid means trying to bring two people together in a romantic relationship. It refers to the idea of matchmaking or helping love to blossom between others.
What virtues does Cupid have?
Cupid shows courage, patience, and the ability to inspire deep emotional connections. His story also demonstrates growth, sacrifice, and emotional maturity.
Is Cupid a fairy or an angel?
Cupid is neither a fairy nor an angel, though he’s sometimes imagined that way today. In Roman myth, he’s a god—a divine being with control over human emotion. That said, his youthful appearance and wings have led to him being mistaken for a cherub or fairy over time.
Study Roman Mythology for £29
If learning about Cupid has sparked your curiosity, there’s so much more to discover. At Centre of Excellence, you can enrol in the Roman Mythology Diploma Course for just £29! Learn about the gods, myths, and legends in greater depth and explore the rich history of the Romans













