Climate change is a global issue affecting every corner of our planet. But what is climate change, and why is it happening? This article will explore the causes, impacts, and solutions to this pressing environmental challenge.
Jump to:
- What is Climate Change?
- What is the Definition of Global Warming?
- What is the Cause of Global Warming?
- What Are the Natural Causes of Climate Change?
- How Do Human Activities Contribute to Climate Change?
- Is the Ocean Also Affected by Climate Change?
- What Does Climate Change Mean for Our Future?
- How Can You Help Combat Climate Change?
- 10 Key Statistics and Facts About Climate Change
What is Climate Change?
Climate change refers to significant changes in global temperatures and weather patterns. While climate fluctuations are a part of Earth's history, recent changes are occurring at an unprecedented rate.
What is the Definition of Global Warming?
Global warming refers to the ongoing and long-term rise in the average temperature of Earth's climate, observed since the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century. It is a key aspect of broader climate change and affects global weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems.
What is the Cause of Global Warming?
Global warming is mainly caused by human activities that release greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide and methane, into the air. These activities include burning fuels like coal and oil, cutting down forests, and various industrial processes, which we will discuss in more detail below.

What Are the Natural Causes of Climate Change?
Contrary to popular belief, climate change isn't solely caused by humans. Nature, too, plays its part, with several natural factors historically contributing. Let's investigate these natural causes and understand their role in shaping our planet's climate."
- Volcanic Eruptions
When volcanoes erupt, they release particles and gases into the atmosphere. Among these, sulphur dioxide is particularly significant as it can form a reflective layer in the atmosphere, reflecting some of the sun’s rays into space. This can lead to a temporary cooling effect on the Earth’s surface.
Historical Example:
The 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora led to the "Year Without a Summer," demonstrating the cooling effect of volcanic eruptions. This event caused significant global temperature drops, leading to agricultural failures and severe weather conditions in many parts of the world.
- Solar Variations
The sun undergoes various activity cycles, including changes in the number and size of sunspots, which can affect the amount of solar energy reaching Earth. Increased solar activity can warm the Earth’s surface slightly, while decreased activity can lead to cooling. These variations, however, are subtle compared to the impacts of human-induced climate change.
Historical Example:
A period between 1645 and 1715, known as the Maunder Minimum, saw an exceptionally low number of sunspots. This coincided with a notably cold era in Europe and North America, often referred to as the "Little Ice Age." This period demonstrated how reduced solar activity could influence colder climates on Earth.
- Earth’s Orbit
Earth’s orbit around the sun is not constant; it changes shape, and the tilt and wobble of Earth's axis also vary. These are known as Milankovitch cycles and happen over thousands of years. These orbital changes can lead to long-term climate shifts, such as ice ages and interglacial periods, by altering the distribution of solar energy on Earth's surface.
Historical Example:
Around 20,000 years ago, Earth experienced the Last Glacial Maximum, where ice sheets covered large parts of the Northern Hemisphere. This was influenced by the Earth’s orbital variations, which reduced the amount of solar energy reaching the higher latitudes, leading to cooler global temperatures and the expansion of ice sheets.

How Do Human Activities Contribute to Climate Change?
While nature has its role in climate change, human activities have become a dominant force driving recent changes. Let's examine how our actions significantly influence Earth's climate, leading to profound and lasting effects.
- Fossil Fuel Combustion
Burning coal, oil, and natural gas for energy is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. This process releases large amounts of carbon dioxide, a key driver of global warming. Major sectors contributing to these emissions include transportation (cars, trucks, planes) and electricity generation.
Historical Example:
The onset of the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century marked a significant increase in the burning of fossil fuels, particularly coal. This era witnessed a noticeable rise in carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, marking the beginning of a significant human impact on global climate.
- Deforestation
Trees play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When forests are cleared, either for timber or to make way for agriculture, this carbon sink is reduced, and significant amounts of carbon dioxide are released. Deforestation also impacts biodiversity and soil quality, further affecting these areas' carbon-absorbing abilities.
Historical Example:
Over the past few decades, large portions of the Amazon Rainforest have been cleared. This deforestation, primarily for agriculture and cattle ranching, has led to a significant loss of one of the Earth's largest carbon sinks, contributing to increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
- Agriculture
Livestock farming, particularly cattle, sheep, and goats, produces methane, a greenhouse gas far more potent than carbon dioxide, though shorter-lived in the atmosphere. Agricultural practices also contribute to climate change through land use changes, including deforestation and soil degradation.
Historical Example:
Post World War II, the Green Revolution introduced intensive agriculture practices worldwide. While it increased food production, it also led to a surge in methane emissions from increased livestock farming and rice paddies, as well as higher nitrous oxide emissions from the heavy use of fertilisers.

- Industrial Processes
Industries, including manufacturing, mining, and construction, release greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, and fluorinated. Industrial activities often consume large amounts of energy, primarily from fossil fuels, adding to carbon emissions.
Historical Examples:
The post-1950s era saw a rapid expansion of industrial activities globally, especially in developing countries. This period is marked by a significant rise in greenhouse gas emissions from various industries, contributing noticeably to the acceleration of climate change.
Understanding these natural and human-driven causes of climate change is essential in addressing the crisis. Each factor plays a role in global climate dynamics, influencing policy decisions and individual actions toward sustainability.
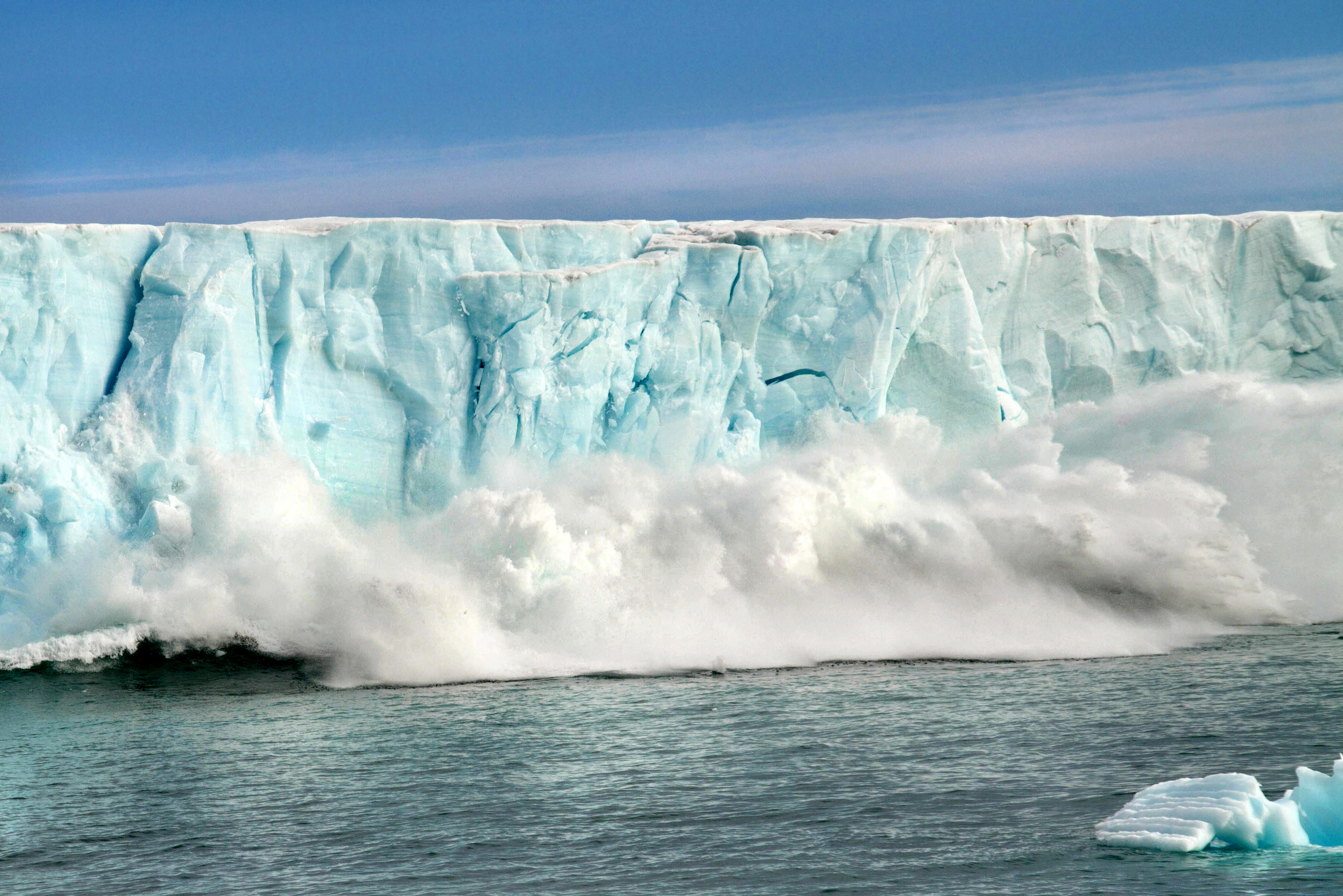
Is the Ocean Also Affected by Climate Change?
Yes, the ocean is affected by climate change. As the Earth's climate warms, oceans absorb excess heat from the atmosphere, leading to increased water temperatures. This warming contributes to ice caps and glaciers melting, causing sea levels to rise.
Additionally, oceans absorb increased carbon dioxide levels from the atmosphere, leading to ocean acidification. This acidification can harm marine life and ecosystems. As oceans warm, the levels of dissolved oxygen decrease, which can affect the biodiversity and health of marine habitats.

What Does Climate Change Mean for Our Future?
Climate change is shaping our future in significant ways. In this section, we'll look at what these changes could mean, touching on everything from the natural world to our daily lives.
- Rising Sea Levels: Melting ice caps and the thermal expansion of seawater threaten coastal communities.
- Weather Extremes: Increased frequency of severe weather events like hurricanes, floods, and droughts.
- Biodiversity Loss: Altered habitats and ecosystems can lead to species decline or extinction.
- Agricultural Impact: Shifts in climate patterns can lead to reduced crop yields and food shortages, affecting food security globally.
- Health Risks: Increased heatwaves and the spread of vector-borne diseases, like malaria, can pose serious health risks to populations.
- Economic Consequences: Climate change can lead to significant economic impacts, including damage to infrastructure and increased costs for climate adaptation and mitigation.
- Water Scarcity: Altered precipitation patterns may result in water shortages in some areas, impacting drinking water supplies and irrigation for agriculture.
- Forced Migration: Rising sea levels and extreme weather events can displace populations, leading to climate refugees and increased social and political challenges.
How Can You Help Combat Climate Change?

Climate change is a global challenge, but each of us holds power to make a difference. In the following section, we'll explore practical and effective ways you can contribute to combating climate change, from everyday habits to broader advocacy and education.
1. Reduce Energy Consumption
Choose energy-efficient appliances that consume less electricity and help reduce your carbon footprint. Simple actions like turning off lights when not in use, using smart thermostats, and properly insulating your home can affect energy usage. Additionally, consider switching to renewable energy sources for your home, such as solar or wind power, which are more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
2. Support Sustainable Choices
Making conscious choices in your daily life can greatly contribute to combating climate change. Choose environmentally friendly products, support sustainable and ethical manufacturing processes, and aim to reduce your overall waste. Recycling and composting are effective ways to manage waste. Also, consider reducing water usage and choosing local and organic food options with a lower carbon footprint.
In our journey to support and inspire positive change, Centre of Excellence takes pride in our commitment to the environment. For every printed course we sell, we plant a tree, contributing actively to reforestation efforts. We have planted over 1,050 trees to date, symbolising our dedication to a greener future.
3. Advocate and Educate
Engaging in advocacy for climate-friendly policies and practices in your community and workplace is crucial. Support initiatives and legislations to reduce carbon emissions and promote renewable energy. Educating yourself and others about the impacts of climate change and how to mitigate them is equally important. Share information, participate in community discussions, and encourage a culture of sustainability and environmental responsibility in your circle of influence.
Each of these actions, while seemingly small, can collectively lead to significant positive impacts on the environment. By adopting more sustainable habits and promoting awareness, you can play an important role in the global effort to combat climate change.
Recommended for you!
Best Sellers10 Key Statistics and Facts About Climate Change
Looking for some quick-fire facts? Here are ten shocking facts and statistics about climate change:
- Global Temperature Rise: The Earth's average temperature has risen by about 1.2 degrees Celsius (2.2 degrees Fahrenheit) since the late 19th century.
- Carbon Dioxide Levels: Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels have reached their highest in human history, surpassing 410 parts per million, a significant increase from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm.
- Ice Loss: The rate of Antarctica ice mass loss has increased by sixfold since the 1980s. Greenland lost an average of 279 billion tons of ice annually between 1993 and 2019.
- Sea Level Rise: Global sea levels have risen about 8 inches in the last century, with the rate in the last two decades nearly doubling that of the last century.
- Ocean Acidification: Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, the acidity of surface ocean waters has increased by about 30%.
- Extreme Events: The number of extreme weather events — such as hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires — has increased significantly, and these events are becoming more intense and frequent due to climate change.
- Climate Refugees: By 2050, climate change could displace 50 million to 1 billion people due to rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and droughts.
- Economic Impact: The economic cost of climate change is vast, potentially costing several trillion dollars in damages globally by the end of the century.
- Heatwaves: The frequency of heatwaves has increased globally, with Europe, for example, experiencing its hottest year on record in 2020.
- Biodiversity Loss: Climate change is a major driver of biodiversity loss. Species are becoming extinct at a rate 1,000 times higher than the natural rate, partly due to changing climates.
Taking Action Together
Climate change is complex, but understanding its causes and effects is the first step towards making meaningful changes. By learning more and taking action, both individually and collectively, we can help lessen its impact.
Expand your knowledge on this topic with our Climate Change Diploma Course. Or study our Geography Diploma Course and Conservation Diploma Course for in-depth insights into physical geography and human impact on the environment.
Unlock an incredible opportunity today! Click on the links above and enrol in any of our transformative courses for the unbeatable price of just £29.